Introduction
In the world of agriculture, a subtle yet significant transformation is taking root, driven by small industrial computers. These unassuming devices are revolutionizing farming practices, offering solutions to age-old challenges. As the global population surges and climate change looms, technology’s role in farming has never been more vital. In this blog, we’ll explore the impact of these small computers on agriculture, from precision farming to resource conservation, highlighting their pivotal role in modernizing and safeguarding our food supply. Welcome to a world where tradition meets innovation, where small industrial computers are quietly reshaping the future of farming.
The Need for Technological Advancements in Agriculture
Challenges Faced by the Agriculture Industry
The agriculture industry stands at a crossroads, facing an array of formidable challenges that threaten food security, sustainability, and economic viability. These challenges include:
- Rising Global Population: With the world’s population steadily increasing, there’s an escalating demand for food. To feed an estimated 9.7 billion people by 2050, agriculture needs to significantly boost production.
- Climate Change: Changing weather patterns, extreme events, and rising temperatures are impacting crop yields and increasing the unpredictability of farming. Droughts, floods, and heatwaves can devastate harvests.
- Resource Scarcity: Depleting arable land and freshwater resources pose substantial limitations on traditional farming practices. Efficient resource utilization is crucial to avoid environmental degradation.
- Pest and Disease Pressure: Crop diseases and pests can decimate entire harvests. With global trade and climate change, invasive species and pathogens are spreading more rapidly than ever.
- Labor Shortages: Many regions face labor shortages in agriculture, particularly for labor-intensive tasks like harvesting. This can lead to increased production costs and reduced competitiveness.

Why Technology is Crucial for Addressing These Challenges
Technology, particularly small industrial computers and their associated innovations, plays a pivotal role in addressing these challenges:
- Precision Agriculture: Small industrial computers enable precision farming techniques that optimize resource use. Through data-driven insights, farmers can apply fertilizers, water, and pesticides more precisely, reducing waste and environmental impact.
- Climate Resilience: Technology provides tools for monitoring weather patterns and predicting extreme events. Farmers can adapt planting and harvesting schedules, and employ climate-controlled systems to protect crops.
- Resource Efficiency: Small industrial computers help manage scarce resources effectively. Smart irrigation systems, for instance, adjust water usage based on real-time data, conserving water while maintaining crop health.
- Early Detection: Advanced sensors and data analysis can identify disease or pest outbreaks in real-time, allowing for targeted responses, reducing crop losses, and minimizing the need for chemical treatments.
- Labor Augmentation: Automation and robotics, driven by industrial computers, can supplement labor shortages. Autonomous vehicles, drones, and robotic harvesters can perform tasks efficiently and without fatigue.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Technology generates vast amounts of data, which when properly analyzed, empowers farmers with actionable insights. This leads to better decision-making, improved crop management, and increased productivity.
In essence, technology is the key to transforming agriculture into a more efficient, sustainable, and resilient industry. Small industrial computers, in particular, form the backbone of these innovations, enabling farmers to tackle the pressing challenges of our time while ensuring that the world’s growing population has access to safe and abundant food supplies.
What Are Small Industrial Computers?
Small industrial computers, or industrial PCs (IPCs), are ruggedized computing devices designed for reliability in harsh industrial environments. These compact machines boast durability, extended lifecycles, and the ability to operate in extreme temperatures and conditions. Their customizability allows adaptation to specific industrial tasks, from automation and control to data acquisition. Unlike consumer-grade PCs, industrial PCs prioritize stability and resilience over aesthetics. They often feature industrial interfaces, such as serial ports and GPIO, crucial for connecting to industrial machinery and sensors. In essence, these specialized computers are the workhorses powering modern industrial automation, ensuring uninterrupted operations in challenging settings.
Key Applications of Small Industrial Computers in Agriculture
a. Precision Farming
Small industrial computers are the brains behind precision farming, facilitating precise management of agricultural activities. They enable:
- Data Analytics: By collecting data from various sources such as GPS, weather stations, and soil sensors, industrial computers process this information to create precise maps of soil conditions, moisture levels, and crop health.
- Automated Equipment: These computers control autonomous machinery like tractors and drones, which can apply fertilizers, pesticides, and water with pinpoint accuracy based on real-time data.
- Benefits: Precision farming enhances efficiency by reducing overuse of resources, leading to lower costs and environmental impact. It optimizes crop yields by tailoring treatments to specific field conditions, ultimately increasing overall productivity.
b. Crop Monitoring and Management
Small industrial computers are invaluable for crop monitoring and management, ensuring healthier crops and higher yields. They facilitate:
- Sensor Integration: Industrial Box PC collect data from various sensors, including moisture sensors, temperature sensors, and cameras, to assess crop conditions.
- Data Fusion: By combining data from sensors and satellite imagery, these computers provide a comprehensive view of crop health, allowing for early detection of diseases, pests, or nutrient deficiencies.

- Precision Spraying: When issues are detected, industrial computers can trigger precise spraying systems to apply treatments only where needed, reducing chemical usage and costs.
c. Livestock Management
Small industrial computers have revolutionized livestock farming by offering advanced monitoring and management tools. They support:
- Animal Tracking: Through RFID tags and sensors, industrial computers monitor the location and movement of livestock, aiding in theft prevention and herd management.
- Health Monitoring: These computers collect data on vital signs, feeding habits, and environmental conditions, allowing farmers to detect early signs of illness or stress in animals.
- Automated Feeding: Industrial PCs can control automated feeding systems to ensure animals receive precise nutrition, optimizing growth and health.
d. Smart Irrigation Systems
Small industrial computers are at the core of smart irrigation, helping optimize water usage in agriculture:
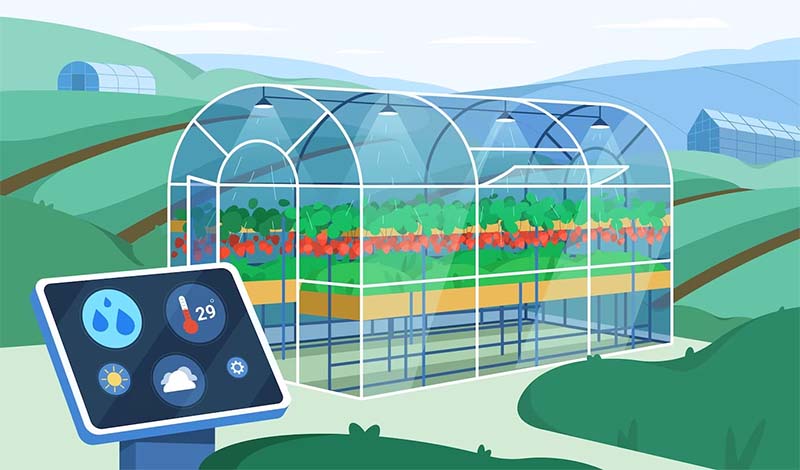

- Weather Data Integration: They gather real-time weather data to adjust irrigation schedules and volumes, preventing over-irrigation during rainy periods.
- Soil Moisture Control: Industrial computers interface with soil moisture sensors to determine when and how much water to apply, preventing both over and under-irrigation.
- Water Distribution: These systems control pumps and valves to distribute water precisely, reducing waste and energy consumption.
Benefits of Small Industrial Computers in Agriculture
a. Increased Efficiency
Small industrial computers are catalysts for efficiency in farming operations:
- Automation: These computers automate tasks like planting, harvesting, and irrigation, reducing the need for manual labor.
- Precision Farming: Through data-driven insights, industrial computers optimize resource allocation, minimizing overuse of water, fertilizers, and pesticides.
- Labor Savings: Automation and precision result in reduced labor requirements, alleviating labor shortages and reducing labor costs.
- Reduced Waste: By precisely applying inputs where needed, industrial computers minimize resource wastage, lowering production costs and environmental impact.
b. Data-Driven Decision Making
Small industrial computers enable farms to harness the power of data analytics:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Industrial PCs collect data on soil conditions, weather, crop health, and more in real-time, providing a comprehensive view of farm operations.
- Predictive Insights: Data analytics identify trends and patterns, enabling predictive modeling for disease outbreaks, weather events, and yield projections.
- Better Planning: Armed with data-driven insights, farmers can make informed decisions on planting, harvesting, and resource allocation, optimizing crop management.
- Cost Reduction: By identifying inefficiencies and optimizing resource use, data-driven decision-making leads to cost reductions and improved profitability.
c. Environmental Impact
Small industrial computers contribute to sustainability in agriculture:
- Reduced Chemical Use: Precision application of pesticides and fertilizers minimizes chemical use, lowering the risk of runoff and soil contamination.
- Water Conservation: Smart irrigation systems, guided by industrial computers, optimize water usage, reducing water waste and promoting conservation.
- Soil Health: By providing data on soil conditions and nutrient levels, these systems help maintain soil health, reducing the need for excessive soil amendments.
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: Lower resource use, reduced waste, and optimized operations contribute to a smaller carbon footprint for agriculture.
- Biodiversity Preservation: By using fewer chemicals and conserving resources, technology-driven farming practices can create healthier ecosystems, promoting biodiversity.
Future Trends
Small industrial computers in agriculture will increasingly leverage AI and robotics, offering AI-powered decision support systems for optimized resource allocation. Automation will expand with autonomous vehicles, drones, and robotic arms, reducing labor costs and improving efficiency. Edge computing will enable real-time data analysis for tasks like weed detection and disease monitoring. Blockchain technology will enhance supply chain transparency, and 5G connectivity will enable seamless remote monitoring. Climate-responsive farming will adapt to changing weather patterns, while advanced sensing technologies will improve crop monitoring. Overall, small industrial computers will drive sustainability, efficiency, and resilience in agriculture through advanced technology adoption.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the integration of small industrial computers into agriculture is revolutionizing the industry, offering a glimpse into a future of smarter, more efficient, and sustainable farming practices. These rugged machines empower farmers with precision tools, AI-driven decision support, and automation, leading to increased yields, reduced labor costs, and minimized environmental impact.
As the agricultural landscape evolves, small industrial computers will continue to play a pivotal role in embracing emerging technologies such as AI, robotics, and edge computing. These advancements will not only address the challenges posed by a growing population and climate change but also ensure a resilient and productive agricultural sector for the future. The synergy between technology and agriculture will shape a brighter, more sustainable future for food production and supply.