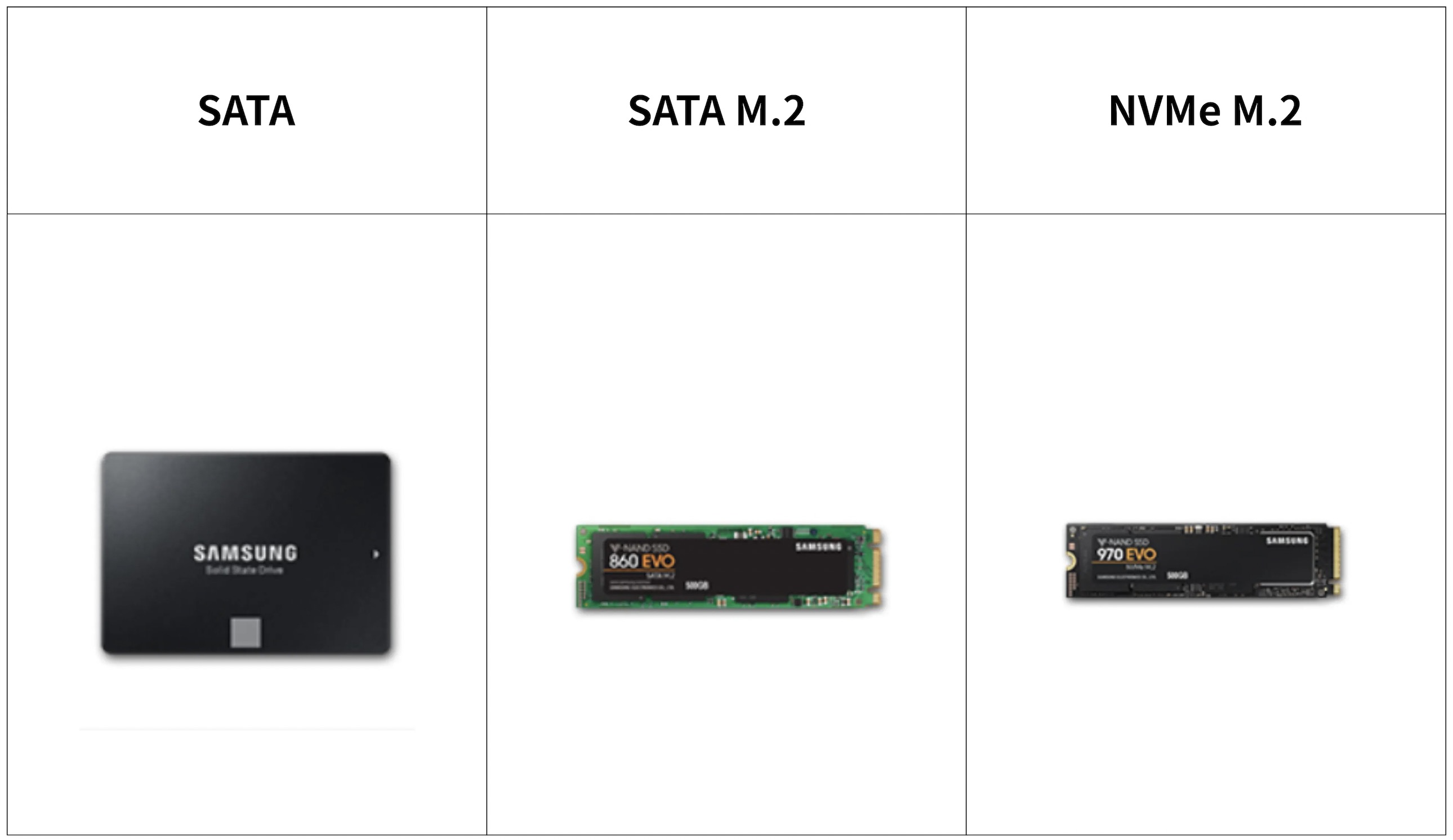
As we all know, SATA has been the main connection method for storage technology. SATA hard drives require two SATA cables to work. One is used to transfer data to the motherboard and the other is used to connect the power supply. Once we use multiple SATA storage drives, cluttered cables are one of big issues that can affect the performance of computer. So, the M.2 SATA form factor SSDs solves this problem by not having the two cable connections used by other SATA storage drives.
M.2 NVME SSDs use the NVMe protocol designed for SSDs. Along with the PCIe bus, M.2 NVMe SSDs can deliver the best performance and fastest speed on the market. M.2 NVMe SSDs utilize PCIe slots to communicate directly with the system CPU. Basically, it allows nand flash to operate as a solid-state drive through a PCIe slot without having to use a SATA communication driver that is much slower than NVMe.
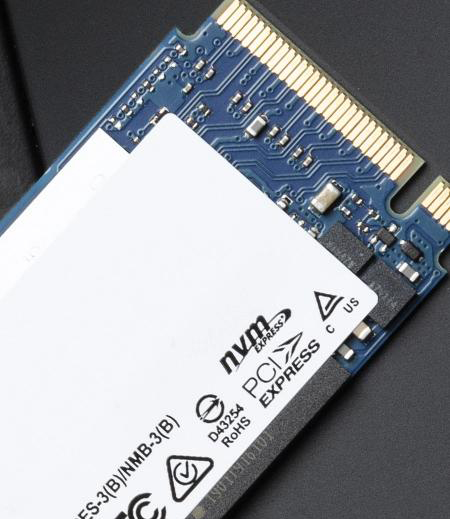
M.2 is a type of interface or slot of the solid state drive. It has two types, one is B type and the other is M type. M.2 SSDs also have different length, such as 2242, 2260, and 2280. The bus standard refers to SATA and PCI-E.
1- Protocol:
M.2 NVME is a high-speed SSD that supports the NVME protocol. It uses the PCI-E bus and its transfer speed is super fast;
M.2 SATA is similar to ordinary SATA, but it is a relatively low-speed SSD;
2- Interface:
M.2 SATA, there are 2 concave pins and three gold fingers; if it is M.2 NVME protocol, it is a concave, two gold fingers;
3- In terms of speed
The NVME that takes the PCI-E channel is currently the fastest.
TAICENN is now delivering TPC-DCS/DRS, TPC-PCS/PRS series Panel PC and TBOX-28X5 Box PC with M.2 NVME storage technology, aim to provide better storage performance for our industrial computing solution and hardware products.